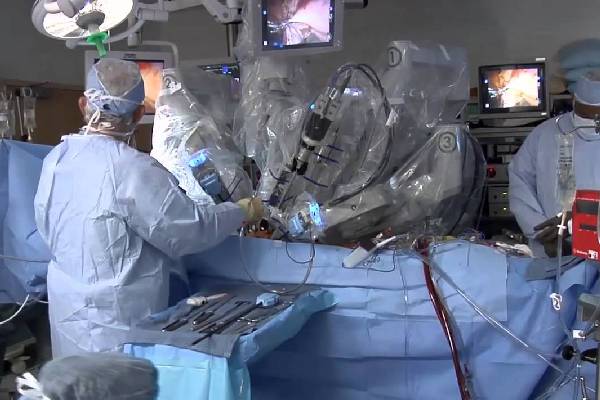
Robotic prostate surgery is also known as a robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy. It is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to treat prostate cancer. The procedure is performed using a robotic surgical system controlled by a surgeon sitting at a console in the operating room. The system is equipped with tiny instruments that mimic the movements of the surgeon’s hands and wrists, allowing for precise and delicate movement.
The robotic surgical system provides several benefits over traditional open surgery. For example, it allows for smaller incisions and less blood loss, resulting in a faster recovery and less post-operative pain. Additionally, the system allows for greater precision and control during the surgery, which can result in fewer complications and better outcomes.
What is the Robotic Prostate Surgery?
The procedure typically begins with the patient being placed under general anesthesia. The surgeon then makes several small incisions in the patient’s abdomen. The surgeon inserts the robotic surgical system’s instruments and a camera through these incisions. The camera provides a magnified, high-definition view of the patient’s prostate, which allows the surgeon to see the area in detail.
Once the instruments and camera are in place, the surgeon uses the robotic system’s controls to move the instruments and remove the prostate gland. The surgery typically takes two to four hours, depending on the case.
After the surgery, the patient will be taken to the recovery room to be monitored. Recovery time can vary depending on the individual case, but most patients can return to normal activities within a few weeks.
Robotic prostate surgery is considered a safe and effective treatment option for prostate cancer. However, as with any surgery, there is always a risk of complications. These can include bleeding, infection, and blood clots. Your surgeon will discuss the specific risks and benefits of the surgery with you before the procedure.
What are the Types of Robotic Prostate Surgery?
There are two main types of robotic prostate surgery: robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy (RALP) and robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (RALRP).
- Robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy (RALP): It is the most common type of robotic prostate surgery. It involves the removal of the entire prostate gland, along with the surrounding tissue, through small incisions in the abdomen. This type of surgery is typically used to treat prostate cancer confined to the prostate.
- Robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (RALRP): It is a variation of RALP. It involves the removal of the entire prostate gland, along with the surrounding tissue, as well as the seminal vesicles and the lymph nodes. This type of surgery is typically used to treat prostate cancer that has spread beyond the prostate.
RALP and RALRP are performed using a robotic surgical system, allowing for greater precision and control during the surgery. The robotic surgical system provides several benefits over traditional open surgery, such as smaller incisions and less blood loss, which can result in a faster recovery time and less post-operative pain.
It’s important to note that other types of robotic surgery can be used to treat prostate cancer, such as cryotherapy, brachytherapy and HIFU. The best type of treatment depends on the stage, location and aggressiveness of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Your urologist or radiation oncologist can recommend the best treatment for your case.
Conclusion
In summary, Robotic Prostate Surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that utilizes a robotic system to treat prostate cancer. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia. The robotic system offers several benefits over traditional open surgery, such as smaller incisions and less blood loss, which can result in a faster recovery time and less post-operative pain. It is considered a safe and effective treatment option for prostate cancer, but as with any surgery, there is always a risk of complications.