Introduction
The night sky has always held a profound fascination for humanity, with its celestial phenomena and cosmic wonders. Among these awe-inspiring events, the lunar eclipse stands out as one of the most captivating and mysterious. In this blog, we will delve into the enchanting world of lunar eclipses, exploring what they are, why they occur, and the cultural significance they hold.
What Is a Lunar Eclipse?
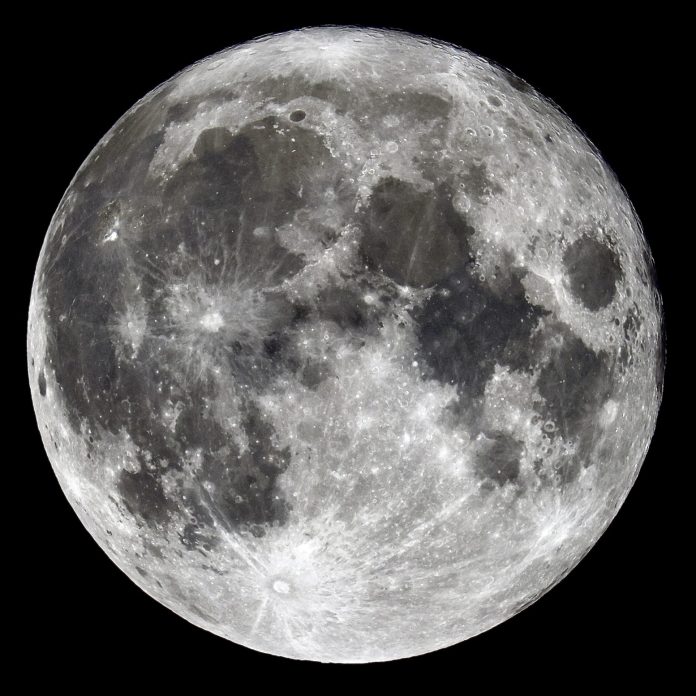
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes directly between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow that gradually engulfs the Moon. Unlike a solar eclipse, which involves the Moon blocking the Sun, a lunar eclipse is visible from a much broader geographic area. When the Earth’s shadow falls on the Moon, it takes on a reddish hue, resulting in the striking phenomenon known as the “Blood Moon.”
Why Do Lunar Eclipses Occur?
The occurrence of a lunar eclipse is a celestial alignment that relies on the relative positions of the Earth, the Moon, and the Sun. Three key components are involved in this captivating event:
- Earth’s Shadow: The Earth casts two distinct shadows: the penumbra (outer shadow) and the umbra (inner shadow). A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes through the Earth’s penumbral and umbral shadows.
- Full Moon: A lunar eclipse can only occur during a Full Moon. This is when the Moon is directly opposite the Sun, allowing it to enter the Earth’s shadow.
- Earth, Moon, and Sun Alignment: For a lunar eclipse to transpire, the Earth, Moon, and Sun must align in a straight line. This alignment results in the Earth obstructing the Sun’s light from reaching the Moon, leading to the eclipse.
Stages of a Lunar Eclipse
A lunar eclipse typically unfolds in several stages:
- Penumbral Phase: The Moon enters the Earth’s penumbral shadow, causing a subtle darkening on one side of the Moon.
- Partial Eclipse: As the Moon progresses into the Earth’s umbral shadow, a noticeable portion of the Moon becomes shaded. This phase can result in captivating partial eclipse views.
- Total Eclipse: When the Moon is entirely within the Earth’s umbral shadow, a total lunar eclipse occurs. During this phase, the Moon takes on the characteristic reddish or coppery glow due to the Earth’s atmosphere scattering and refracting sunlight.
- Reversal of Stages: The lunar eclipse unfolds in reverse order, with the Moon gradually moving out of the Earth’s umbral and penumbral shadows.
Cultural Significance of Lunar Eclipses
Lunar eclipses have captured the human imagination for millennia and hold cultural and symbolic significance in various societies. Many ancient civilizations regarded lunar eclipses as omens or supernatural events. In some cultures, lunar eclipses were believed to herald impending change, while in others, they were associated with deities and rituals.
In modern times, lunar eclipses continue to inspire awe and wonder. They are often considered excellent opportunities for stargazing, astrophotography, and meditation. Many people come together to witness this celestial spectacle and celebrate the beauty of the cosmos.
Conclusion
Lunar eclipses are breathtaking celestial events that bridge the realms of science and wonder. They remind us of the intricate dance of the Earth, Moon, and Sun and their profound impact on our night sky. Whether for scientific exploration or cultural significance, lunar eclipses serve as a reminder of the boundless mysteries the universe holds, waiting to be uncovered and admired. So, the next time a lunar eclipse graces the night sky, don’t forget to look up and witness this mystical dance of shadows.